|
|
CIV E 445 - APPLIED HYDROLOGY
SPRING 2009 - MIDTERM 2 - SOLUTION
|
|
PROBLEM 3: ESSAY QUESTIONS
|
-
1 sq mi.
- The time of concentration is a function of L (length), n (roughness), S (slope), and i (rainfall intensity).
- m = 1.667 = 5/3.
- The four variables (or parameters) of the runoff curve number method are:
- Hydrologic soil group: A, B, C, D.
- Land use and treatment class: agricultural, urban, range, forest.
- Ground surface condition: poor, fair, good
- Antecedent Moisture Condition: I, II, III.
- The Horton abstraction model is (a) substractive, (b) cause-effect (more infiltration leads to less runoff),
(c) bottomless (infinite soil depth).
The Mockus (runoff curve number) abstraction model is: (a) additive, (b) cybernetic (biofeedbacks; more inflitation lead to more
runoff), (c) has finite soil depth.
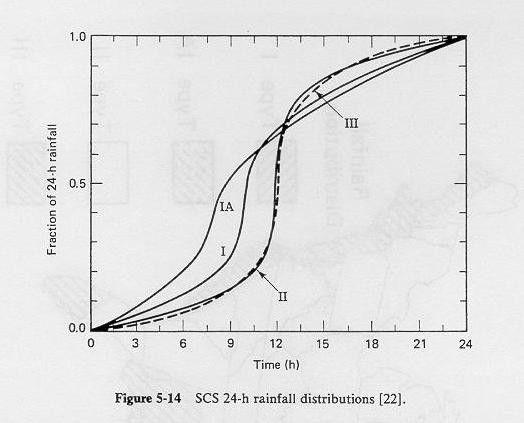
- The NRCS Type II storm, which covers the internal continental U.S.,
excluding the Eastern seaboard, the coast of the Gulf of Mexico,
and the Pacific Coast.

- According to the Gumbel method, the return period of the mean annual flood is 2.33 years.
- Around the middle of the climatic spectrum, say 800 mm of mean annual precipitation.
Example: the state of Idaho, where droughts have a tendency to last longer.
- The correlation coefficient for this case would be zero.
- Levees help protect rivers from overflowing their banks more frequently.
However, disadvantages are:
- they provide a false sense of security as
floods increase in magnitude and frequency with upstream development,
- when they fail, the results are usually catastrophic,
- they starve the floodplain of nutrients, and
- they produce the loss of "the sight of the river."
|