|
|
CIVE 445 - ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
SPRING 2010 - MIDTERM 1 - SOLUTION
|
a. What is the Bowen ratio?
-
The ratio between sensible heat, transferred to the atmosphere by convection and conduction,
and latent heat, i.e., the heat used in the evaporation process.
b. What is albedo? What is the albedo of the Amazon rainforest? What is the albedo of the Sahara desert??
c. What is the difference between potential and actual evapotranspiration?
- Potential evapotranspiration occurs under an ample supply of moisture.
- Actual evapotranspiration occurs in reality, when moisture may be limited.
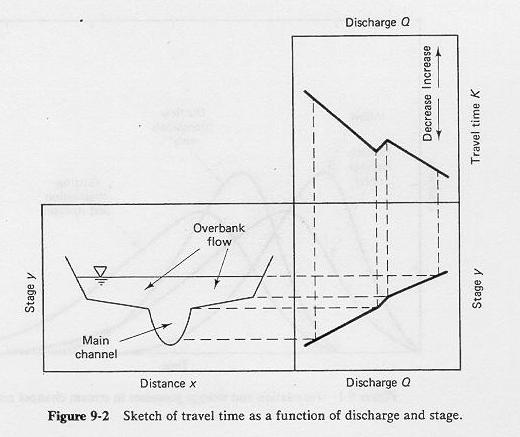
d. How does time of concentration vary with flood stage? Draw a sketch for a wide range of flood stages.
-
low flow: time of concentration is long
- high inbank flow: time of concentration reduces
- low overbank flow: time of concentration increases
- high overbank flow: time of concentration decreases
e. What do the Creager curves depict?
- They depict the diffusion that is present in streamflow.
- The Creager curves state that the greater the catchment area,
the smaller the peak flow per unit of catchment area.
f. To what five factors is to be attributed the recurrence of debris flows in the San Gabriel
Mountains of Northeast Los Angeles? State them in causal order.
- The uplift (through tectonism) of the mountain range (reported to be
the highest in the U.S.).
- The type of vegetative ecosystem (mediterranean, chaparral), which has developed adaptations
to survive through droughts, including waxed leaf surfaces to minimize evapotranspiration.
The mediterranean ecosystem
occurs in midlatitudes (30o-35o) that have exposure to
westerlies (trade winds from
the west).
- The wind storms (Santa Ana), which affects the region.
- The wildland fires, propelled by drought and wind,
which recur approximately every thirty years in chaparral ecosystems. The fires vaporize the waxy substances
(in the litter and standing biomass) at the surface,
and condense 1-5 cm inside the soil, creating the hydrophobic soil layer.
- The intense rainfall events, exceeding 1 in/hr,
which follow the fire because of enhanced coalescence in the lower atmosphere due to ash particles
produced by the fire.
Problem 1
|